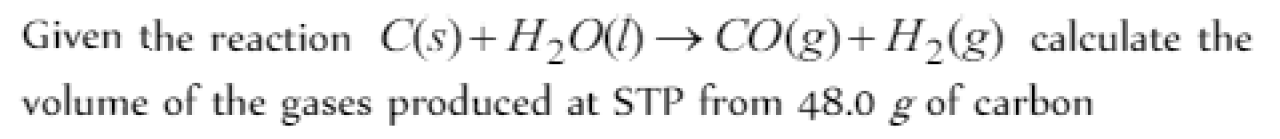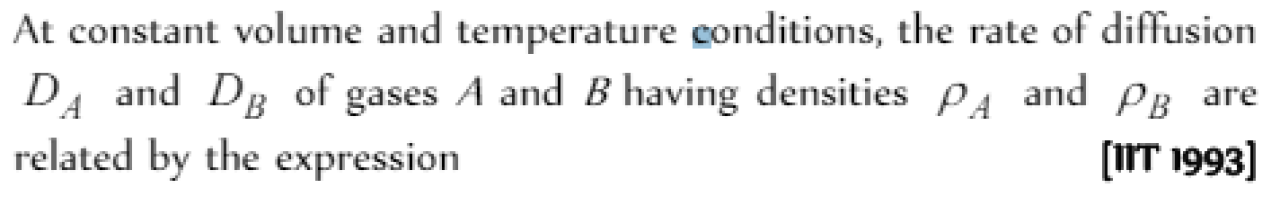Question#1
Correct ideal gas equation is MDCAT2024
Question#2
Intermolecular forces between molecules of Ideal gas are MDCAT-2024
Question#3
Equation of Boyle's law is [DPMT 2005]
Question#4
At what temperature, the sample of neon gas would be heated to double of its pressure, if the initial volume of gas is/are reduced to 15% at 75o C [Kerala CET 2005]
Question#5
If the absolute temperature of an ideal gas become double and pressure become half, the volume of gas would be [Kerala CET 2005]
Question#6
The pressure and temperature of 4dm3 of carbon dioxide gas are doubled. Then the volume of carbon dioxide gas would be [KCET 2004]
Question#7
Question#8
A certain mass of gas occupies a volume of 300 c.c. at 27oC and 620 mm pressure. The volume of this gas at 47o C and 640 mm pressure will be [MH CET 2003]
Question#9
A cylinder of 5 liters capacity, filled with air at NTP is connected with another evacuated cylinder of 30 liters of capacity. The resultant air pressure in both the cylinders will be [BHU 2004]
Question#10
A mixture of NO2 and N2O4 has a vapour density of 38.3 at 300K . What is the number of moles of NO2 in 100g of the mixture [Kerala PMT 2004]
Question#11
Containers A and B have same gases. Pressure, volume and temperature of A are all twice that of B, then the ratio of number of molecules of A and B are [AFMC 2004]
Question#12
At what pressure will a quantity of gas, which occupies 100 ml at a pressue of 720 mm , occupy a volume of 84 ml [DPMT 2004]
Question#13
Hydrogen diffuses six times faster than gas A . The molar mass of gas A is [KCET 2004]
Question#14
The rate of diffusion of hydrogen gas is [MH CET 2003; Pb. CET 2000]
Question#15
How will you separate mixture of two gases [AFMC 2004]
Question#16
One litre oxygen gas at STP will weigh [Pb. CET 2004]
Question#17
The maximum number of molecules is present in [CBSE PMT 2004]
Question#18
What is the ratio of diffusion rate of oxygen and hydrogen [Pb. CET 2003]
Question#19
At NTP, the density of a gas, whose molecular weight is 45 is [Pb. CET 2001, 03]
Question#20
At S.T.P. 1g CaCO3 on decomposition gives CO2 [Pb. CET 2000]
Question#21
When a jar containing gaseous mixture of equal volumes of CO2 and H2 is placed in a solution of sodium hydroxide, the solution level will [Pb. CET 2001]
Question#22
At constant temperature and pressure which gas will diffuse first H2 or O2? [Pb. CET 2000]
Question#23
At what pressure a quantity of gas will occupy a volume of 60 ml , if it occupies a volume of 100ml at a pressure of 720mm ? (while temperature is constant) : [Pb. CET 2000]
Question#24
Which of the following gas mixture is not applicable for Dalton’s law of partial pressure [Pb. CET 2002]
Question#25
If the four tubes of a car are filled to the same pressure with N2 , O2 , H2 and Ne separately, then which one will be filled first [Manipal PMT 2000]
Question#26
A closed vessel contains equal number of nitrogen and oxygen molecules at a pressure of P mm. If nitrogen is removed from the system then the pressure will be [MP PMT 1985]
Question#27
Who among the following scientists has not done any important work on gases [Bihar MADT 1980]
Question#28
Five grams each of the following gases at 87o C and 750 mm pressure are taken. Which of them will have the least volume [MNR 1991]
Question#29
A pre-weighed vessel was filled with oxygen at N.T.P. and weighted. It was then evacuated, filled with SO2 at the same temperature and pressure, and again weighted. The weight of oxygen will be [NCERT 1989]
Question#30
The vapour density of a gas is 11.2. The volume occupied by 11.2 g of this gas at N.T.P. is [MNR 1982; CBSE PMT 1991]
Question#31
A bottle of cold drink contains 200 ml liquid in which CO2 is 0.1 molar. Suppose CO2 behaves like an ideal gas, the volume of the dissolved CO2 at STP is [CBSE PMT 1991]
Question#32
The energy of an ideal gas depends only on its
Question#33
The volume of 4.4 g of CO2 at NTP is [Pb. CET 1997]
Question#34
There are 6.02x1022 molecules each of N2, O2 and H2 which are mixed together at 760 mm and 273 K. The mass of the mixture in grams is [Pb. PMT 1997]
Question#35
Question#36
4.4 g of a gas at STP occupies a volume of 2.24 L, the gas can be [Haryana CEET 2000]
Question#37
Question#38
At what temperature, the rate of effusion of N2 would be 1.625 times that of SO2 at 50o C [CBSE PMT 1996]
Question#39
X ml of H2 gas effuses through a hole in a container in 5 seconds. The time taken for the effusion of the same volume of the gas specified below under identical conditions is [IIT 1996]
Question#40
The rate of diffusion of methane at a given temperature is twice that of X. The molecular weight of X is [MNR 1995; Kerala CEE 2001]
Question#41
Two grams of hydrogen diffuse from a container in 10 minutes. How many grams of oxygen would diffuse through the same container in the same time under similar conditions [MNR 1980]
Question#42
A gas diffuses at a rate which is twice that of another gas B. The ratio of molecular weights of A to B is [EAMCET 1986]
Question#43
If 4 g of oxygen diffuses through a very narrow hole, how much hydrogen would have diffused under identical conditions [CPMT 1971]
Question#44
Which of the following pairs will diffuse at the same rate through a porous plug [EAMCET 1990]
Question#45
A bottle of ammonia and a bottle of dry hydrogen chloride connected through a long tube are opened simultaneously at both ends, the white ammonium chloride ring first formed will be[IIT 1988]
Question#46
Atmolysis is a process of
Question#47
Question#48
The densities of two gases are in the ratio of 1 : 16. The ratio of their rates of diffusion is [CPMT 1995]
Question#49
If rate of diffusion of A is 5 times that of B, what will be the density ratio of A and B [AFMC 1994]
Question#50
The densities of hydrogen and oxygen are 0.09 and 1.44 g L-1. If the rate of diffusion of hydrogen is 1 then that of oxygen in the same units will be [RPMT 1994]
Question#51
Molecular weight of a gas that diffuses twice as rapidly as the gas with molecular weight 64 is [EAMCET 1994]
Question#52
The molecular weight of a gas which diffuses through a porous plug at 1/6th of the speed of hydrogen under identical conditions is [EAMCET 1990]
Question#53
A gas diffuses 1/5 times as fast as hydrogen. Its molecular weight is [CPMT 1992; Bihar CEE 1982]
Question#54
The ratio of the rate of diffusion of a given element to that of helium is 1.4. The molecular weight of the element is [Kerala PMT 1990]
Question#55
According to Grahman's law at a given temperature, the ratio of the rates of diffusion rA / rB of gases A and B is given by [IIT 1998]
Question#56
Which of the following relationships is correct, where r is the rate of diffusion of a gas and d is its density [CPMT 1994]
Question#57
Which of the following gas will have highest rate of diffusion [Pb. CET Sample paper 1993; CPMT 1990]
Question#58
Rate of diffusion of a gas is [IIT 1985; CPMT 1987]
Question#59
Equal amounts of two gases of molecular weight 4 and 40 are mixed. The pressure of the mixture is 1.1 atm. The partial pressure of the light gas in this mixture is [CBSE PMT 1991]
Question#60
To which of the following gaseous mixtures is Dalton's law not applicable
Question#61
Which of the following mixtures of gases does not obey Dalton's law of partial pressure [CBSE PMT 1996: Kerala PMT 2000]
Question#62
Dalton's law of partial pressure will not apply to which of the following mixture of gases [Bihar MADT 1981]
Question#63
If three unreactive gases having partial pressures PA , PB, and PC and their moles are 1, 2, and 3 respectively then their total pressure will be [CPMT 1994]
Question#64
“Equal volumes of all gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal number of particles.” This statement is a direct consequence of [Kerala MEE 2002]
Question#65
The total pressure exerted by a number of non-reacting gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the gases under the same conditions is known as [CPMT 1986]
Question#66
A sample of gas occupies 100 ml at 27o C and 740 mm pressure. When its volume is changed to 80 ml at 740 mm pressure, the temperature of the gas will be [Vellore CMC 1991]
Question#67
The density of a gas at 27o C and 1 atm is d. Pressure remaining constant at which of the following temperatures will its density become 0.75 d [CBSE PMT 1992]
Question#68
A wheather balloon filled with hydrogen at 1 atm and 27o C has volume equal to 12000 liters. On ascending it reaches a place where the temperature is -23o C and pressure is 0.5 atm. The volume of the balloon is [CBSE PMT 1991]
Question#69
One litre of a gas weighs 2 g at 300 K and 1 atm pressure. If the pressure is made 0.75 atm, at which of the following temperatures will one liter of the same gas weigh one gram [CBSE PMT 1992]
Question#70
At N.T.P. the volume of a gas is found to be 273 ml. What will be the volume of this gas at 600 mm Hg and 273o C [CPMT 1992]
Question#71
Pure hydrogen sulphide is stored in a tank of 100-litre capacity at 20o C and 2 atm pressure. The mass of the gas will be [CPMT 1989]
Question#72
16 g of oxygen and 3 g of hydrogen are mixed and kept at 760 mm pressure and 0o C. The total volume occupied by the mixture will be nearly [Vellore CMC 1991]
Question#73
Two separate bulbs contain ideal gases A and B. The density of gas A is twice that of gas B. The molecular mass of A is half that of gas B. The two gases are at the same temperature. The ratio of the pressure of A to that of gas B is [BHU 1994]
Question#74
Correct gas equation is [CBSE PMT 1989; CPMT 1991]
Question#75
At 0o C and one atm pressure, a gas occupies 100 cc. If the pressure is increased to one and a half-time and temperature is increased by one-third of absolute temperature, then final volume of the gas will be [DCE 2000]
Question#76
Volume of 0.5 mole of a gas at 1 atm. pressure and 273K is [EAMCET 1992]
Question#77
How many moles of He gas occupy 22.4 litres at 30o C and one atmospheric pressure [KCET 1992]
Question#78
If two moles of an ideal gas at 546 K occupy a volume of 44.8 liters, the pressure must be [NCERT 1981; JIPMER 1991]
Question#79
For an ideal gas number of moles per liter in terms of its pressure P, gas constant R, and temperature T is [AIEEE 2002]
Question#80
Gas equation PV = nRT is obeyed by [BHU 2000]
Question#81
S.I. unit of gas constant R is [CPMT 1994]
Question#82
The correct value of the gas constant R is close to [CBSE PMT 1992]
Question#83
Select one correct statement. In the gas equation, PV = nRT [CBSE PMT 1992]
Question#84
The constant R is [Orissa 1990]
Question#85
Which one of the following indicates the value of the gas constant R [EAMCET 1999]
Question#86
In the equation PV = nRT , which one cannot be the numerical value of R [BIT 1987]
Question#87
In the ideal gas equation, the gas constant R has the dimensions of [NCERT 1982
Question#88
In the equation of state of an ideal gas PV = nRT , the value of the universal gas constant would depend only on [KCET 2005]
Question#89
The compressibility of a gas is less than unity at STP. Therefore [IIT 2000]
Question#90
Which one of the following statements is false [Manipal PMT 1991]
Question#91
In a closed flask of 5 liters, 1.0 g of H2 is heated from 300 to 600 K. which statement is not correct [CBSE PMT 1991]
Question#92
“One gram molecule of a gas at N.T.P. occupies 22.4 liters.” This fact was derived from [CPMT 1981, 1995]
Question#93
Two closed vessels of equal volume containing air at pressure P1 and temperature T1 are connected to each other through a narrow tube. If the temperature in one of the vessels is now maintained at T1 and that in the other at T2, what will be the pressure in the vessels
Question#94
The pressure p of a gas is plotted against its absolute temperature T for two different constant volumes, V1 and V2. When V1 > V2 , the
Question#95
400 cm3 of oxygen at 27o C were cooled to -3o C without change in pressure. The contraction in volume will be
Question#96
A certain sample of gas has a volume of 0.2 liter measured at 1 atm. pressure and 0o C. At the same pressure but at 273o C, its volume will be [EAMCET 1992, 93; BHU 2005]
Question#97
Pressure remaining the same, the volume of a given mass of an ideal gas increases for every degree centigrade rise in temperature by definite fraction of its volume at [CBSE PMT 1989]
Question#98
A 10 g of a gas at atmospheric pressure is cooled from 273o C to 0o C keeping the volume constant, its pressure would become
Question#99
Use of hot air balloons in sports and meteorological observations is an application of [Kerala MEE 2002]
Question#100
Which of the following expression at constant pressure represents Charle's law [AFMC 1990]
Question#101
At constant pressure, the volume of fixed mass of an ideal gas is directly proportional to [EAMCET 1985]
Question#102
Densities of two gases are in the ratio 1 : 2 and their temperatures are in the ratio 2 : 1, then the ratio of their respective pressures is [BHU 2000]
Question#103
Which of the following graphs represent Boyle's law
Question#104
Which of the following statement is false [BHU 1994]
Question#105
If 20 cm3 gas at 1 atm. is expanded to 50 cm3 at constant T, then what is the final pressure [CPMT 1988]
Question#106
Air at sea level is dense. This is a practical application of [Kerala CEE 2000]
Question#107
At constant temperature, in a given mass of an ideal gas [CBSE PMT 1991]
Question#108
If P, V, T represent pressure, volume and temperature of the gas, the correct representation of Boyle's law is [BIT Ranchi 1988]
Question#109
Which of following gases has lowest density under room temperature? MDCAT2023
Question#110
Ideal gas equation NUMS-2021
Question#111
Amount of energy required to increase temperature of 1.2x1024molecules from 273K to 274k is
Question#112
An ideal gas will have maximum density when [CPMT 2000]
Question#113
If P, V, M, T and R are pressure, volume, molar mass, temperature and gas constant respectively, then for an ideal gas, the density is given by [CBSE PMT 1989, 91]
Question#114
Absolute zero is unattainable. The current attempts have resulted in temperature as low as MDCAT2009
Question#115
100 dm3 at 3atm pressure and 27oC is transferred to a chamber of 300dm3 maintained at a temperature of 327oC. what will be pressure of chamber? MDCAT2008
Question#116
The ideal gas equation is PV=nRT the symbol n in S.I unit represents ETEA-2008 med
Question#117
If absolute temperature of a gas is doubled and pressure is increased four times then the volume becomes ETEA-2015 Med
Question#118
If we want to raise the temprature of one mole of an ideal gas by 1K we have to provide how much amount of energy ? MDCAT2022
Question#119
Which of following is the correct equation to calculate relative molar mass of gas MDCAT2018
Question#120
According to general gas equation the density of an ideal gas depends upon MDCAT2020
Question#121
Identify the value of R at STP MDCAT2017
Question#122
A 10L flask contains 64g of oxygen at 27oC. the pressure inside the flask in bar is (R=0.0831barK-1mol-1 )NEET2022
Question#123
In the equation of sate of an ideal gas PV = nRT , the value of the universal gas constant would depend only on [KCET 2005]
Question#124
If two moles of an ideal gas at 546 K occupy a volume of 44.8 litres,
the pressure must be
[NCERT 1981; JIPMER 1991]
Question#125
For an ideal gas number of moles per litre in terms of its pressure P,
gas constant R and temperature T is
[AIEEE 2002]
Question#126
Gas equation PV=nRT is obeyed by [BHU 2000]
Question#127
The constant R is [Orissa 1990]
Question#128
In the equation
PV=nRT
, which one cannot be the numerical
value of R [BIT 1987]
Question#129
In the ideal gas equation, the gas constant R has the dimensions of [NCERT 1982}
Question#130
In the equation of sate of an ideal gas
PV = nRT
, the value of the
universal gas constant would depend only on
[KCET 2005]