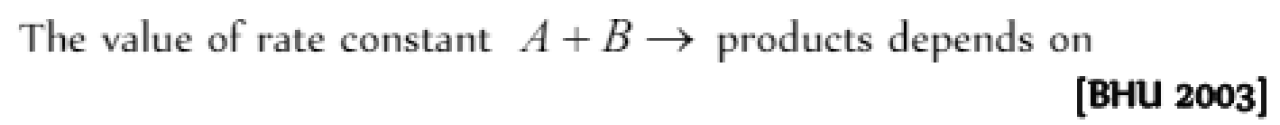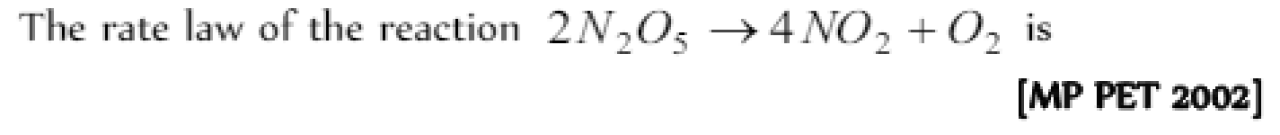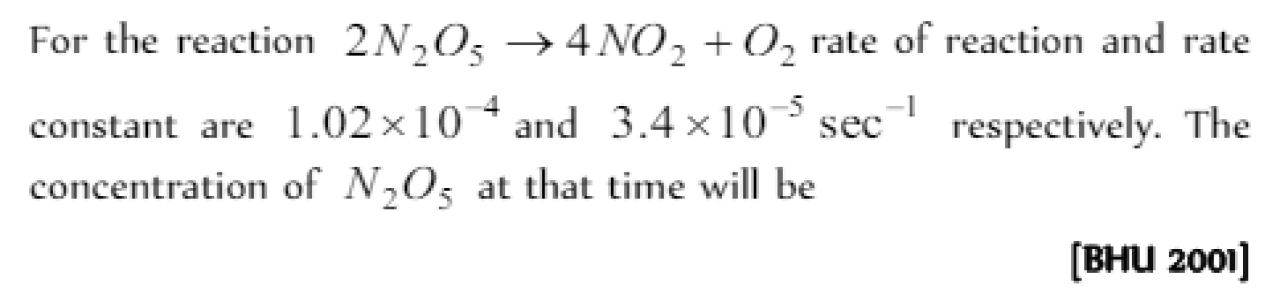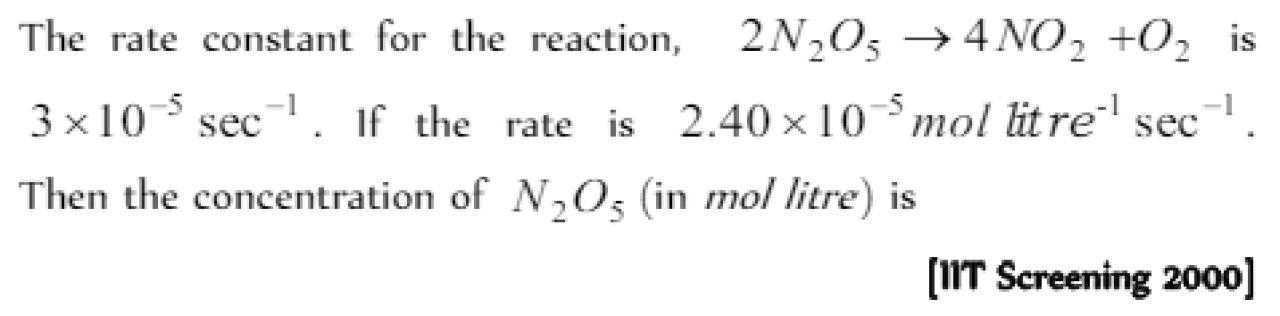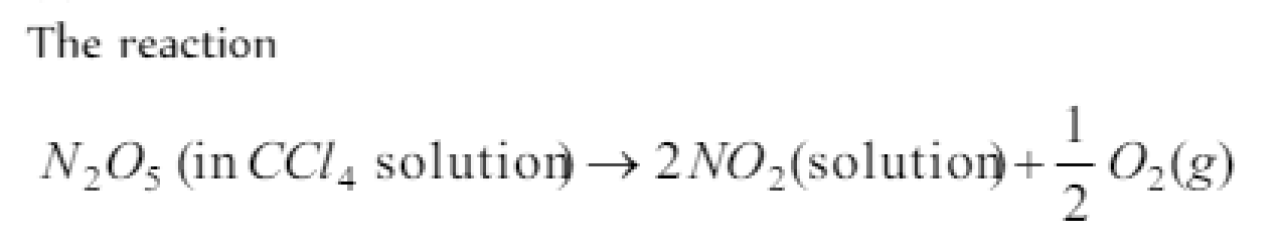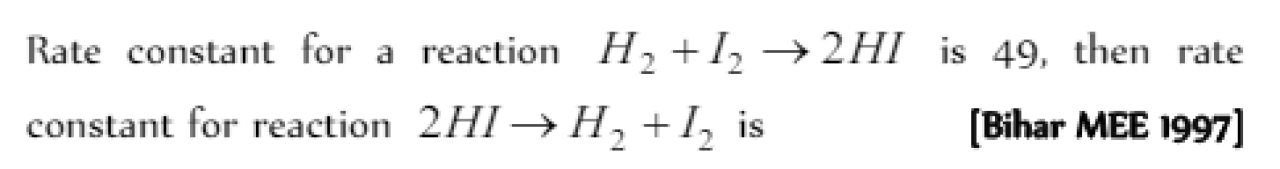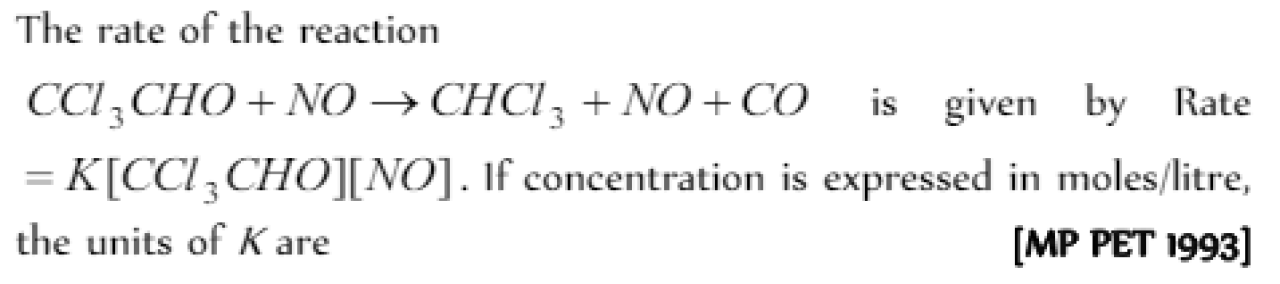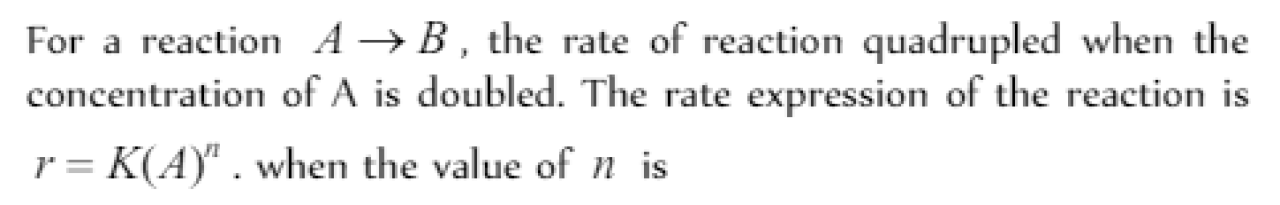Home/Reaction kinetics
Velocity constant or rate constant( K)
Question#1
The specific rate constant of a first-order reaction depends on the [IIT 1981, 83; DPMT 1991; Bihar MEE 1995; KCET 1998]
Question#2
Question#3
The rate constant of a reaction depends upon [BHU 2004]
Question#4
Question#5
If R = K [NO]2 [O2] rate constant may be increased by [BHU 2003]
Question#6
Question#7
Question#8
Question#9
Question#10
Question#11
Question#12
Question#13
The rate of reaction is determined by slow step reaction. The step is called
Question#14
Which of the following oxides of nitrogen will be the most stable one [NCERT 1978]
Question#15
Question#16
The velocity constant of a reaction is K. Which of the following statements is not true regarding K
Question#17
Question#18
Question#19
The rate constant of a reaction depends on [CPMT 1989; DPMT 2001]
Question#20
Point out the wrong statement :
For a first order reaction
Question#21
Velocity constant K of a reaction is affected by
Question#22
Question#23
Question#24
he reaction 2NO (g) + O2 (g) ? 2 NO2 (g) is of first order. If volume of reaction vessel is reduced to 1/3, the rate of reaction would be [MP PMT 2001]
Question#25
Question#26
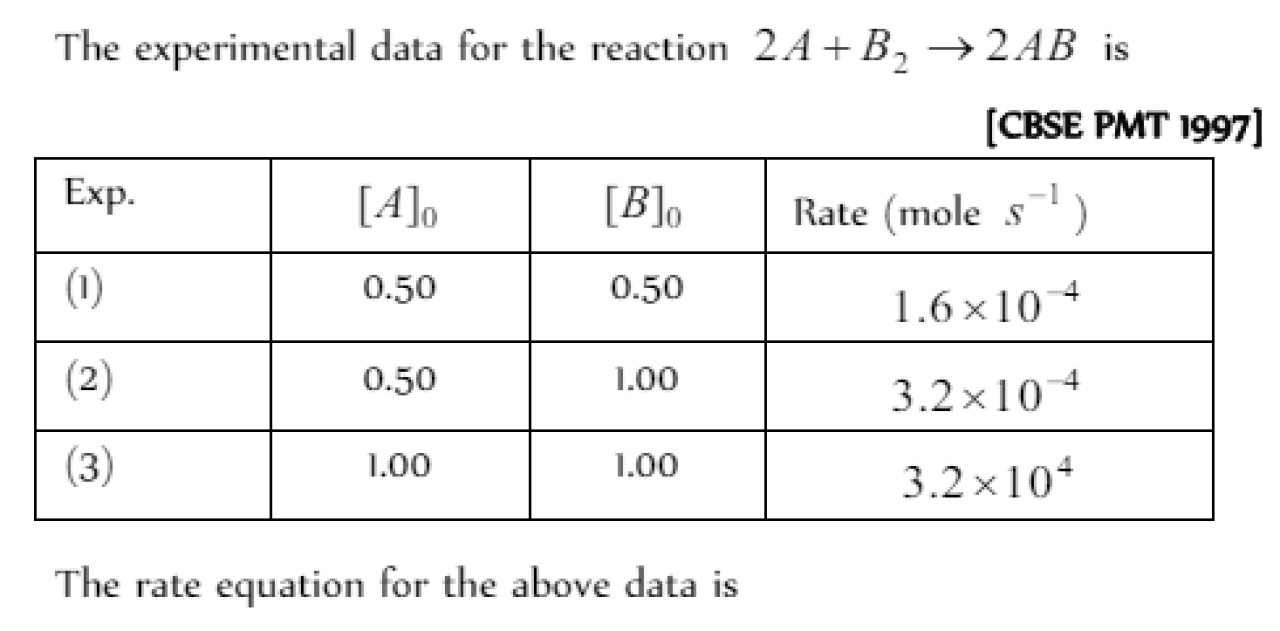
The rate law corresponds to the above data is
Question#27
Question#28
Question#29
Question#30
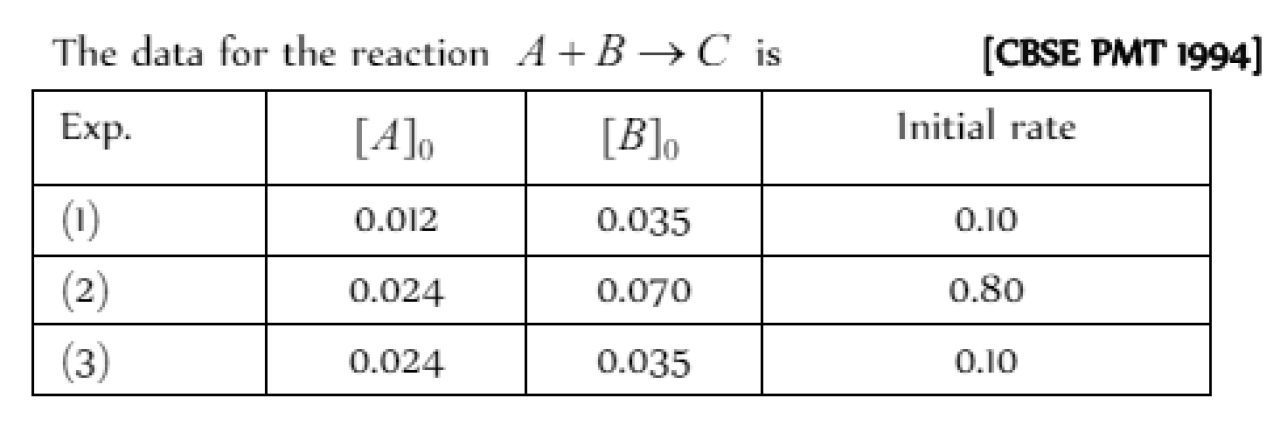
The rate law for reaction A + 2B = C + 2D will be
Question#31
Which of these does not influence the rate of reaction [KCET 2005]
Question#32
Unit of rate constant is same as for NUMS2021
Question#33
The unit of rate constant is same as that of rate of reaction in NUMS2019
Question#34
Unit of K in first order reaction is MDCAT2017
Question#35
The unit of rate constant for a zero order reaction is {2011Mains}
Question#36
For the following reaction scheme (homogeneous), the rate constant
has units : A + B → C
[MP PET 1999]