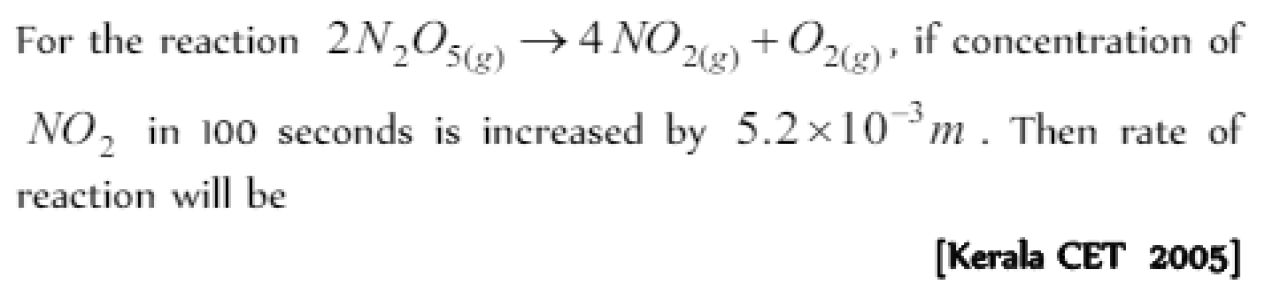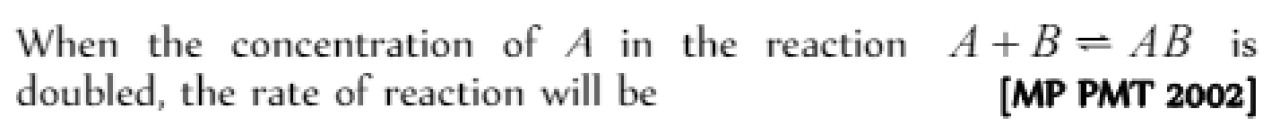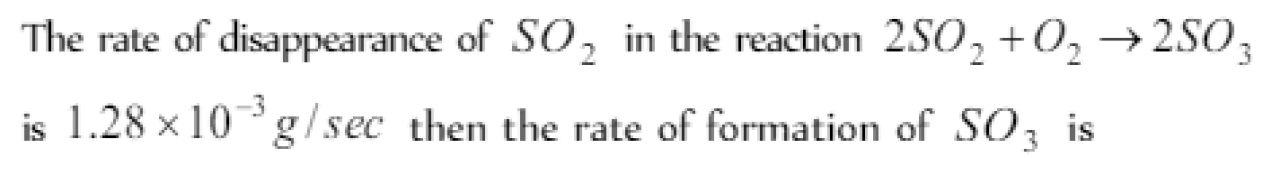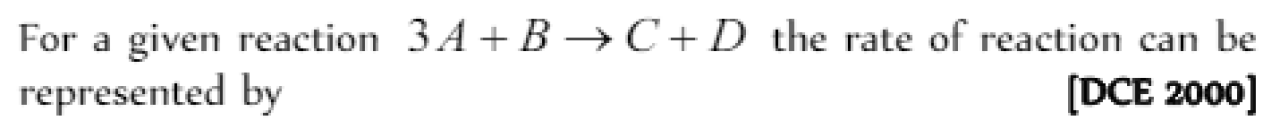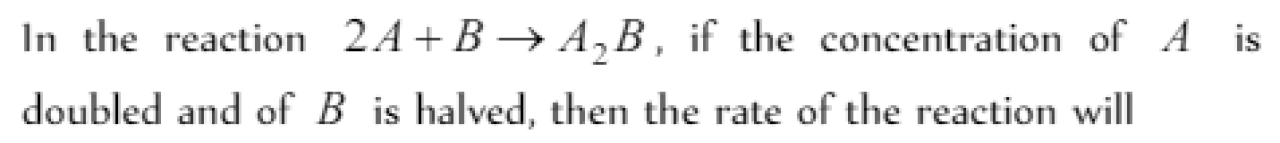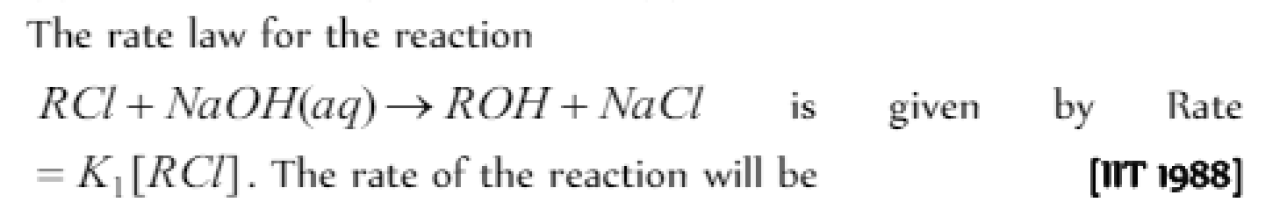Home/Reaction kinetics
Rate of reaction
Question#1
A first order reaction complete its 10% in 20 minutes then time required to complete its 19% is [Kerala CET 2005]
Question#2
Question#3
Rate of reaction [Pb. CET 2004]
Question#4
In which of the following cases, does the reaction go farthest to completion [UPSEAT 2001]
Question#5
The velocity constant of a reaction at 290 K was found to be 3.2 x 10-3 . At 300 K it will be [MP PMT 2004]
Question#6
Which reaction characteristics are changing by the addition of a catalyst to a reaction at constant temperature
(i) Activation energy
(ii) Equilibrium constant
(iii) Reaction entropy
(iv) Reaction enthalpy
[DCE 2003]
Question#7
A reaction is catalysed by ‘X ’. Here ‘X ’ [MP PMT 2003]
Question#8
Which of the following statements is false in relation to enzyme [MP PMT 2003]
Question#9
The rate of a reaction [CPMT 1973]
Question#10
The main function of a catalyst in speeding up a reaction is
Question#11
The temperature coefficient of a reaction is
Question#12
Velocity constant of a reaction at 290 K was found to be 3.2 x 10-3. At 310 K it will be about [KCET 1989, 91]
Question#13
A catalyst increases the rate of a chemical reaction by [MNR 1988; CPMT 1999; Pb. PMT 2000]
Question#14
The rate of a reaction is doubled for every 10o rise in temperature. The increase in reaction rate as a result of temperature rise from 10o to 100o is [KCET 1993; Kerala PET 2002; MP PET 2003]
Question#15
The temperature coefficient for reaction in which food deteriorates is 2. Then food deteriorates ...... times as rapidly at 25oC as it does at 5oC
Question#16
An increase in temperature by 10oC generally increases the rate of a reaction by [MP PET 1994; CBSE PMT 2000]
Question#17
The velocity of the chemical reaction doubles every 10oC rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50oC, the velocity of the reaction increases to about
Question#18
Question#19
Question#20
The rate of a chemical reaction depends upon [AFMC 2002]
Question#21
Question#22
Question#23
Question#24
The rate of a reaction depends upon the [Pb. PMT 1999]
Question#25
Question#26
Question#27
Question#28
A catalyst increases the rate of reaction because it [EAMCET 1992]
Question#29
The rate of a gaseous reaction is given by the expression K[A][B]. If the volume of the reaction vessel is suddenly reduced to 1/4th of the initial volume, the reaction rate relating to original rate will be[Roorkee 1992]
Question#30
Question#31
Question#32
Time required for completion of ionic reactions in comparison to molecular reactions is
Question#33
If the concentration of the reactants is increased, the rate of reaction [MP PMT 1989]
Question#34
In a catalytic conversion of N2 to NH3 by Haber's process, the rate of reaction was expressed as change in the concentration of ammonia per time is 40 x 10-3 mollitre-1 s-1. If there are no side reaction, the rate of the reaction as expressed in terms of hydrogen is (in mollitre-1 s-1 )
Question#35
When a reaction is progressing
Question#36
The concentration of a reactant decreases from 0.2 M to 0.1 M in 10 minutes. The rate of the reaction is
Question#37
The rate of chemical reaction at constant temperature is proportional to
Question#38
If doubling the concentration of a reactant `A' increases the rate 4 times and tripling the concentration of `A' increases the rate 9 times, the rate is proportional to [AIIMS 1991]
Question#39
Question#40
The rate at which a substance reacts depends on its [MP PMT 1987; BHU 1999; KCET 2005]
Question#41
The rate of a reaction that not involve gases is not dependent on [CPMT 1988; AFMC 1995]
Question#42
The rate of a chemical reaction [MP PMT 1973; CPMT 1982]
Question#43
The rate of a chemical reaction depends upon [AFMC 2002]
Question#44
A gaseous hypothetical chemical \( 2A \leftrightarrow 4B +C \) is carried out in a closed vessel. The concentration of B is found to increase by 5 x 10-3 mol l-1 in 10 second. The rate of appearance of B is [AFMC 2001]
Question#45
For the reaction \( N_2 + 3H_2 \rightarrow 2NH_3 \) if \( \frac{\Delta[NH_3]}{\Delta t} \) =2 x 10-4 mol l- s- , the value of \( -\frac{\Delta H_2}{\Delta t} \) would be [MP PMT 2000]
Question#46
For a given reaction \( 3A + B \rightarrow C + D \) the rate of reaction can be represented by [DCE 2000]
Question#47
The term \( -\frac{dt}{dc} \) in a rate equation refers to the [MP PMT 1996]
Question#48
For the reaction \( N_2 + 3 H_2 \rightarrow 2NH_3 \) g under certain conditions of temperature and partial pressure of the reactants, the rate of formation of NH3 is 0.001 kg h-1 . The rate of conversion of H2 under the same conditions is [IIT 1994]
Question#49
How will be the rate of reaction, if the slop of the curve is greater near the start of reaction. MDCAT2023
Question#50
Rate of reaction between two specific time intervals is called [MDCAT2023]
Question#51
Which is not true about rate of reaction ? NUMS2021
Question#52
When the change in concentration is 6 x 10-4moldm-3 and time for that change in 10 seconds, the rate of reaction will be MDCAT2015
Question#53
The reaction rate in forward direction decreases with the passage of time because MDCAT2012
Question#54
The term \(\frac{-\Delta [A]}{\Delta t} \)in a rate equation refers to the
[MP PMT 1996]
Question#55
The rate of a gaseous reaction is given by the expression K[A][B]. If the volume of the reaction vessel is suddenly reduced to 1/4th of the initial volume, the reaction rate relating to original rate will be[Roorkee 1992]
Question#56
If the concentration of the reactants is increased, the rate of reaction
[MP PMT 1989]
Question#57
If doubling the concentration of a reactant `A' increases the rate 4
times and tripling the concentration of `A' increases the rate 9
times, the rate is proportional to [AIIMS 1991]
Question#58
The rate at which a substance reacts depends on its
[MP PMT 1987; BHU 1999; KCET 2005]
Question#59
The rate of a reaction that not involve gases is not dependent on [CPMT 1988; AFMC 1995]
Question#60
The rate of a chemical reaction [MP PMT 1973; CPMT 1982]