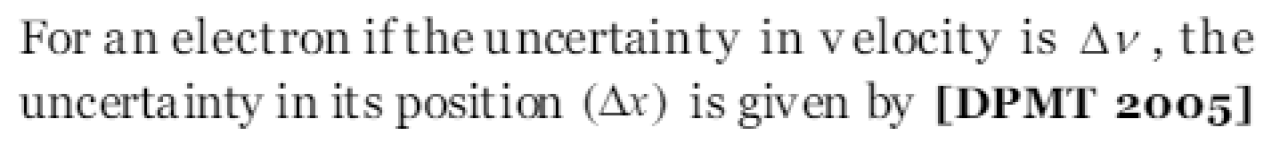Home/Atomic Strcuture
Uncertainty principle
Question#1
Question#2
According to Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle, the product of uncertainties in position and v elocities for an electron of mass kg 9.1 x 10-31 kg is
Question#3
Uncertainty in the position of a 0.25 g particle is 10-5. Uncertainty of velocity is ( h = 6.63 x10-34 Js ) [A IEEE 2002]
Question#4
The uncertainty in the momentum of an electron is 1 x 10-5 kg m / s. The uncertainty in its position will be ( h = 6.63 x10-34 Js ) [Pb. CET 2000]
Question#5
Question#6
The uncertainty in the position of a moving bullet of mass 1 0 gm is m 10-5m. Calculate the uncertainty in its velocity [DCE 1999]
Question#7
The uncertainty principle and the concept of wave nature of matter was proposed by ...... and ...... respectively [MP PET 1997]
Question#8
If uncertainty in the position of an electron is zero, the uncertainty in its momentum would be [CPMT 1988]
Question#9
Simultaneous determination of exact position and momentum of an electron is [BHU 1979]
Question#10
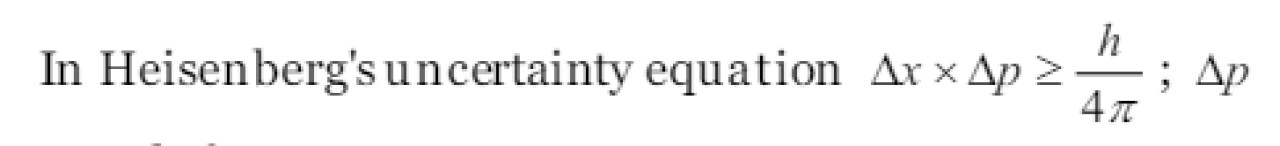
Question#11
“The position and velocity of a small particle like electron cannot be simultaneously determined.” This statement is [NCERT 1979; BHU 1981, 87]
Question#12
According to Heisenberg uncertainty principle [A MU 1990; BCECE 2005]
Question#13
The uncertainty principle was enunciated by [NCERT 1975; Bihar MEE 1997]